If you are a parent or a health-conscious adult, it is normal to pause before saying yes to dental sealants. You want to know what actually touches your child’s new molars, how long it stays there, and whether it is safe for a growing body. When you search what are dental sealants made of, you are really asking if the protection against cavities is worth any possible exposure to plastics or chemicals in those deep grooves and pits.
At Sunshine Dentistry, we believe you deserve straight, detailed answers before any preventive treatment goes ahead. In this guide, we explain what are dental sealants made of, how these materials are tested and what current research says about safety. We choose BPA-free sealants whenever possible and review manufacturers’ data in line with Canadian guidelines, so your Richmond Hill dentist can confidently recommend options that match your family’s values as well as your oral health needs.
What Are Dental Sealants Made of Exactly
Most modern dental sealants are made from a carefully engineered resin that behaves like a liquid plastic before it is set. The main sealant materials include a resin matrix, tiny filler particles that make the coating stronger, and special photo initiators that harden when exposed to a curing light. When you ask what are dental sealants made of, you are really asking how stable these components are once they have bonded to enamel.
In many Canadian practices, you will see two main types used. Resin-based dental sealants create a smooth, durable barrier on chewing surfaces, while glass ionomer sealants release small amounts of fluoride that support enamel in high-risk patients. Both types are designed to sit on the outer surface of the tooth, so this sealant composition works as a shield rather than entering deeper tissues.
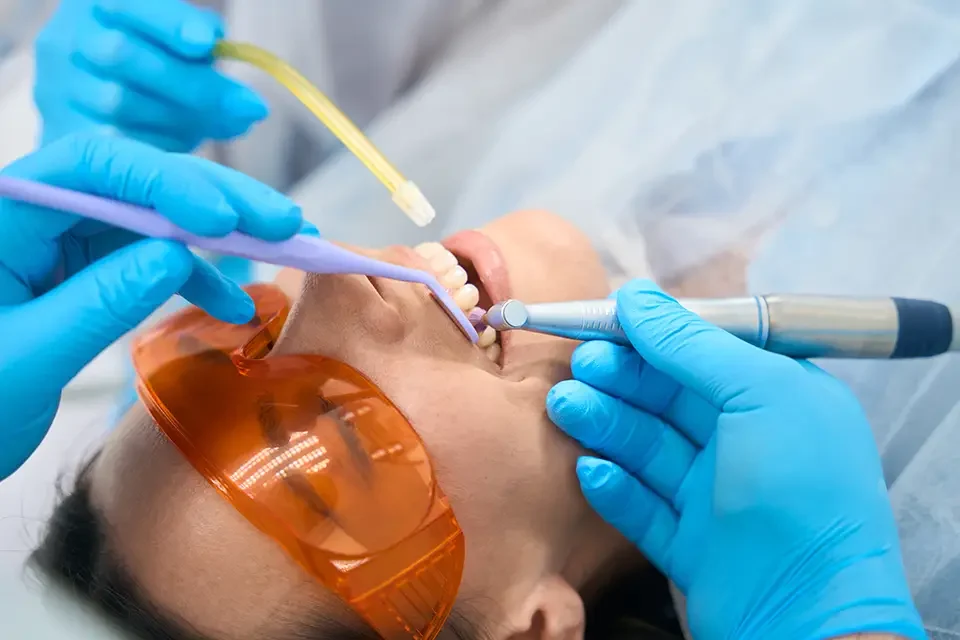
Are Dental Sealants Safe and Truly Non-Toxic
Parents often ask not only what are dental sealants made of, but also whether the coating on their child’s teeth is safe for long-term use. Large clinical studies and guidance from major dental organisations support that are dental sealants safe for routine cavity prevention when used as directed. The cured material is designed to be stable, so non-toxic sealants stay on the surface of the enamel, and help block food and bacteria from sitting in deep grooves where decay usually starts.
At Sunshine Dentistry, we look carefully at the safety profile of every product before it is used on patients. Whenever possible, we select BPA-free dental sealants, follow strict placement and curing protocols, and polish away any residual surface film. Your Richmond Hill dentist will also ask about allergies, medical conditions, and your comfort level, then review alternatives so you can make an informed decision that fits your family’s health priorities.
Who Is a Good Candidate for Dental Sealants?
Not every tooth needs dental sealants, but some smiles are clearly at higher cavity risk and benefit a lot from this extra layer of protection.
- Children and teens whose first and second molars have just erupted and show deep chewing grooves that trap food.
- Adults with a history of decay in back teeth or early enamel changes that keep returning in the same areas.
- Patients with braces or limited dexterity who find thorough brushing difficult and have persistent plaque buildup on molars.
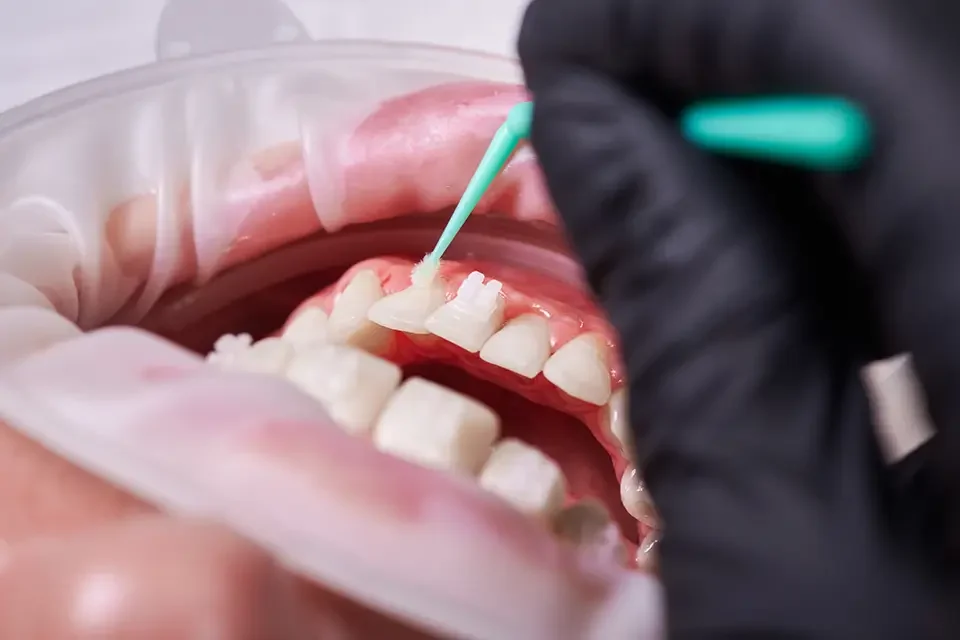
How the Dental Sealant Procedure Works Step by Step?
For most patients, the sealant procedure feels quick and comfortable, and it usually fits easily into a regular check-up visit. Children can breathe normally, talk between steps, and stay fully awake the entire time.
- Your dentist gently cleans the tooth surface so no food or plaque is sealed in.
- A mild etching gel is placed for a short time to help dental sealants grip the enamel.
- The tooth is rinsed and dried, then kept away from saliva while the material is applied.
- A thin layer of sealant material is flowed into the grooves and set with a curing light.
- Finally, your bite is checked and adjusted so that chewing still feels natural and easy.
How Long Dental Sealants Last and How to Care for Them
Most patients are surprised by how long dental sealants last when they are checked regularly. In many cases, the coating protects the chewing surface for four to seven years, sometimes longer in low-risk mouths. Your dentist will look closely at each sealant during routine exams and let you know if a small repair or a full replacement of the sealant material is needed.
At home, you can help sealants stay intact with simple habits. Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, floss once daily, and try not to bite ice, pens, or very hard candy, since these can chip both enamel and the protective layer. If a tooth suddenly feels rough or catches your nail, mention it to your Richmond Hill dentist so the sealant can be smoothed or refreshed.
Talk to a Richmond Hill Dentist about Dental Sealants
If you are still unsure about what are dental sealants made of or how they fit into your family’s prevention plan, a face-to-face conversation can be very reassuring. At Sunshine Dentistry, your Richmond Hill dentist will look at your child’s cavity risk, review current research, and show you exactly where dental sealants could help protect back teeth. You can also ask specific questions about brands, ingredients, and safety.
During your visit, we can combine sealant assessment with a routine check-up to make appointments easier for busy families. Our team will explain fees, possible insurance coverage, and how long the visit is likely to take. If dental sealants are a good fit for you or your child, we will schedule treatment at a time that feels comfortable and convenient.
FAQs
Are dental sealants really necessary if my child brushes well?
Even with good brushing, back teeth often have deep grooves that trap food and bacteria where bristles cannot reach. Dental sealants cover those tiny pits, so plaque cannot sit there and start a cavity. For many children, sealants simply add an extra layer of protection on top of a good home routine.
What about BPA? Are dental sealants non-toxic?
Parents who ask what are dental sealants made of are usually worried about chemicals. Modern products used in Canada are carefully regulated, and many are BPA-free dental sealants. Any trace amounts, if present, are extremely low and drop quickly after placement. Your dentist can check ingredient sheets and suggest the safest option for your family.
How long do sealants last, and what if one comes off?
With regular check-ups, dental sealants often protect molars for several years. If part of a sealant chips or wears away, it can usually be repaired or replaced during a routine visit, so the tooth does not lose its protection.